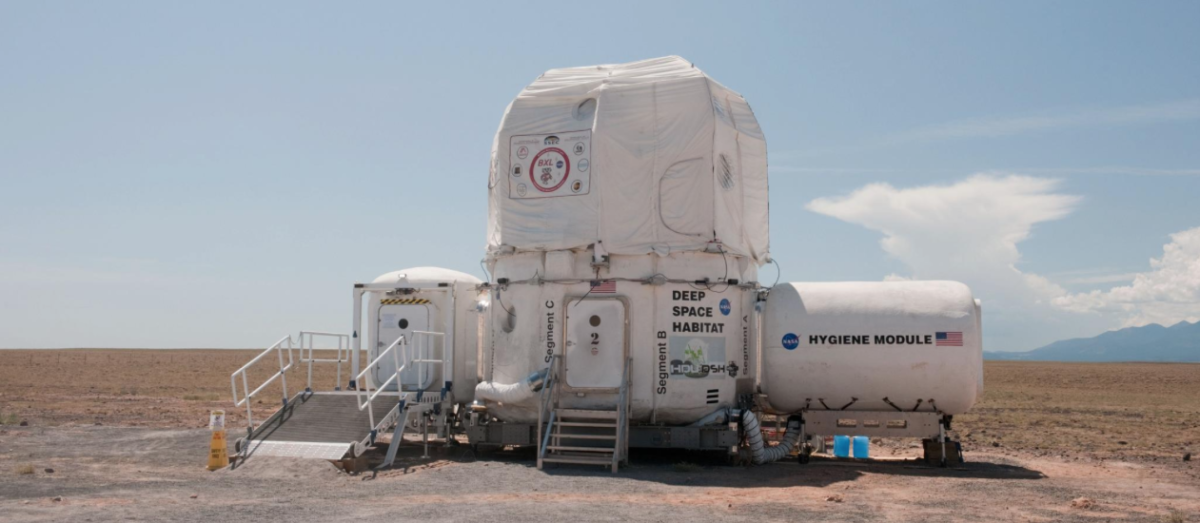
Have you ever considered how astronauts live in space and how their habitat is engineered to support their lives? Currently the International Space Station has housed astronauts since 2000. NASA is now looking at deep-space Habitats. While the International Space Station can quickly get supplies from Earth because it is so close, deep space missions require more significant planning and engineering. Life support systems will need to be able to recycle carbon dioxide from breathing 98% of the water consumed and 75% of oxygen. Any loaded item must be carefully packaged to be recycled, repurposed, and reused as a top priority.
The Space Habitats include many habitation systems, such as life support, environmental monitoring, radiation protection, etc. The structure of the Space Habitats, also called habitation modules, will house the habitation systems and serve as the home for many astronauts shortly. NASA is currently involved with the U.S. industry to find ways to refine concepts and develop prototypes.
The evolution of Artificial Intelligence has been remarkable for deep-space Habitats. Artificial Intelligence can use computing, algorithms, machine learning, and robotics. It can process astronomical data, detect patterns, uncover concealed connections, and more. Artificial Intelligence will also be able to help control spacecraft, collect and analyze data, and perform experiments on samples. Using Artificial Intelligence, we can understand far more than we do now.
Related Stories:
- https://www.sciencedirect.com/topics/physics-and-astronomy/space-habitat
- https://www.astronomy.com/space-exploration/heating-and-cooling-space-habitats-isnt-easy-one-engineering-team-is-developing-a-lighter-more-efficient-solution/
- https://www.nasa.gov/humans-in-space/deep-space-habitation-overview/
- https://researchoutreach.org/articles/how-could-we-build-liveable-space-habitat/
- https://parametric-architecture.com/the-evolution-of-ai-in-space-exploration-and-habitat-engineering/
Take Action: