Undiscovered Creatures Beneath Antarctic Waters Revealed After Iceberg Breaks Away
A recent phenomenon in Antarctica has led to the groundbreaking discovery of previously unknown marine life beneath the icy depths of the Southern Ocean. The rupture of a massive iceberg from the Antarctic Peninsula’s ice shelf has reshaped the landscape and revealed hidden ecosystems that have remained undisturbed for centuries. These discoveries give us new angles into the secret life beneath the ice and could significantly impact our understanding of how life survives in extreme conditions.
A Shocking Breakaway
The iceberg, known as A-68, broke off from the Larsen C Ice Shelf in 2017, one of the largest such events in recent history. The A-68, roughly the size of Chicago, broke away from the Antarctic ice sheet, exposing a seabed hidden from sunlight for decades. Following its departure, the newly exposed waters provided scientists a unique opportunity to study the previously inaccessible marine environments beneath the ice. These waters had been covered by thick ice for years, preventing sunlight from penetrating and limiting the ecosystems below. With the iceberg gone, scientists have explored the newly revealed areas, discovering thriving marine life previously hidden from human eyes.

Unexpected Discoveries
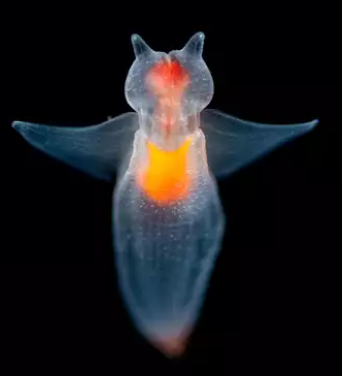
In the wake of this event, marine biologists from multiple institutions embarked on research expeditions, uncovering an astonishing variety of creatures. According to reports from Scientific American, species such as giant sponges, sea anemones, and other benthic organisms have been thriving in waters isolated from the outside world for millions of years (Science American, 2025). These creatures, many previously unknown to science, appear uniquely adapted to survive in the harsh conditions of deep Antarctic waters.
The Wired report highlights the particular interest in these findings, noting how these creatures have adapted to life beneath nearly half a mile of ice, surviving with minimal light and under immense pressure. “We had no idea how many species were living there,” one researcher noted, emphasizing the excitement of discovering such well-preserved ecosystems (Wired, 2025).
Thriving Ecosystems
One of the most incredible aspects of this discovery is the variety of life in such an extreme environment. According to the Schmidt Ocean Institute, ecosystems around the iceberg’s breakaway point have shown rich biodiversity, with multiple species of fish, invertebrates, and other organisms that thrive in the cold waters. The iceberg’s detachment has provided researchers with a rare opportunity to study the dynamics of Antarctic marine ecosystems that have been isolated from human activity for thousands of years.
This finding is significant not only for marine biology but also for broader scientific questions about how ecosystems can survive and adapt to changing environmental conditions. These creatures have evolved under conditions of complete darkness, extreme cold, and isolation from the rest of the world’s oceans, which provides a unique perspective on how life could potentially exist in similar environments elsewhere, such as beneath the icy moons of Jupiter and Saturn.
Related stories:
- https://www.scientificamerican.com/article/stunning-antarctic-sea-creatures-discovered-after-iceberg-breaks-away/
- https://www.foxweather.com/earth-space/iceberg-breaks-away-antarctica-discoveries
- https://www.discoverwildlife.com/animal-facts/marine-animals/hidden-life-beneath-antarctic-peninsula-ice-sheet
- https://www.wired.com/story/scientists-discover-strange-creatures-under-a-half-mile-of-ice/
- https://schmidtocean.org/thriving-antarctic-ecosystems-found-in-wake-of-recently-detached-iceberg
Take Action: