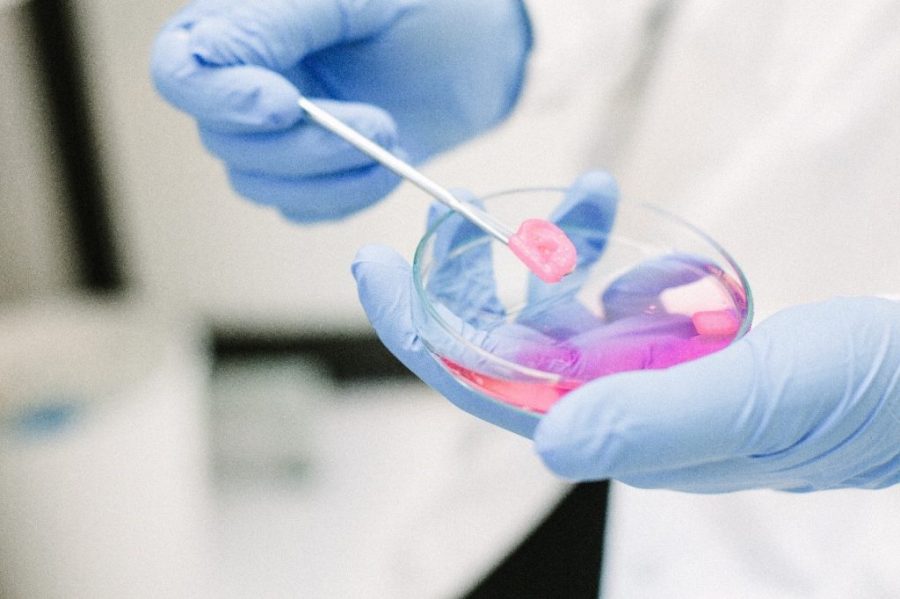
Imagine a future where damaged organs can be repaired, not with transplants from deceased donors, but with tissues engineered from your own cells. This futuristic vision is becoming a reality thanks to the emerging field of bioprinting.
Bioprinting is a type of 3D printing that uses living cells and biomaterials to create functional tissues. Similar to a traditional 3D printer that builds objects layer by layer, a bioprinter deposits precise amounts of bio ink, a mixture of cells and supporting materials, to create a 3D structure.
This technology holds immense potential for revolutionizing medicine. Bio printed tissues could be used for a variety of applications, including:
- Skin grafts: Bio printed skin could be used to treat burn victims or patients suffering from large skin wounds.
- Organs for transplantation: Bioprinting could potentially address the critical shortage of donor organs for transplants.
- Drug testing: Bio printed tissues could be used to test the effects of new drugs on human cells before clinical trials.
While bioprinting is still in its early stages, significant progress has been made. Scientists have successfully bio printed tissues such as skin, cartilage, and even blood vessels.
Challenges remain, however. One major hurdle is ensuring the viability and functionality of the bio printed tissues. Researchers are working on developing methods to create complex structures that mimic the natural organization of tissues in the body. Additionally, the development of a wider range of bio inks compatible with different cell types is needed.
Despite the challenges, the potential benefits of bioprinting are undeniable. This technology has the potential to transform medicine, offering new hope for patients with organ failure and tissue damage. As research continues, bioprinting is poised to play a major role in the future of healthcare.
Related Stories:
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC10261138/
https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S2352320421000444
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC10451845/
Take Action: