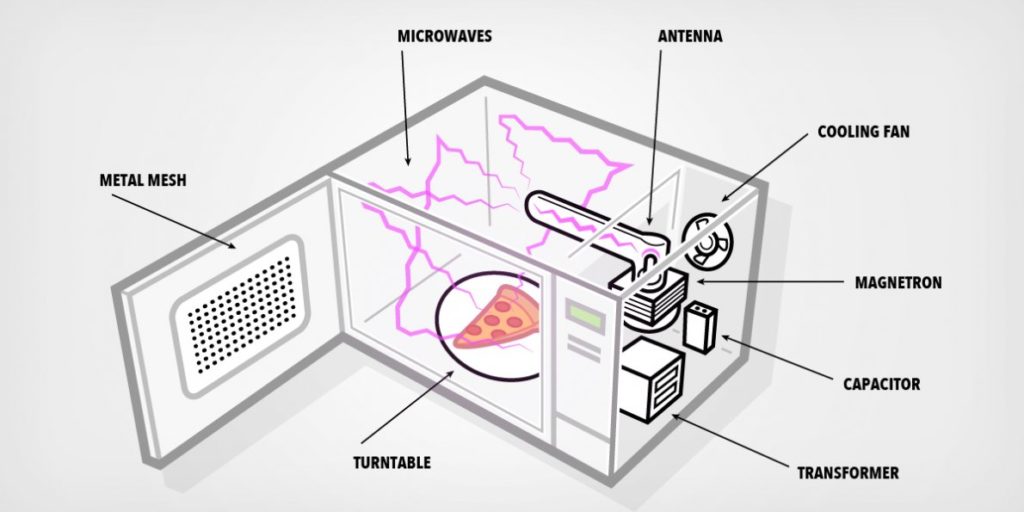
How Do Microwaves Work
Microwaves Prepare Food Remarkably Quickly. But How Does This Invention Work?
While longer than infrared radiation and shorter than radio waves, Microwaves are around 12 cm from crest to crest. This means that most foods can easily absorb microwaves. However, unlike X-rays or ultraviolet rays, microwave particles don’t have enough energy to damage molecules and cause cancer. This is good to know when making a dish in a microwave, but have you ever wondered how it actually works?
An essential part of how microwave ovens cook is the magnetron, which produces electromagnetic microwaves. When turned on, a transformer changes the 120 volts of typical household energy from a wall socket to 4,000 volts or more to power the magnetron. The magnetron’s central filament becomes heated by the voltage, spitting off electrons. In about 2 seconds, The food compartment is then bombarded with microwaves. Water, fat, and sugar are easily absorbed by the 2.45 gigahertz microwave frequency, which allows the waves to penetrate deep into the food and heat them up. That’s why Solids without water don’t heat up in microwaves.
These electromagnetic waves influence water molecules by twisting them back and forth. The ends of water molecules do this because they are each positively and negatively charged. The negatively charged end of the water molecule points away from the electric field of the microwave, while the positively charged end attempts to align itself with it. However, the field reverses 2.5 billion times per second, which causes the molecule to be rapidly twisted. The molecules scrape against one another as they spin back and forth Friction builds up, which results in the production of heat. Which cooks the food. A microwave cooks food considerably more quickly than a traditional oven because it simultaneously heats the inside and outside of the food at once. This contrasts with a typical oven or frying pan, in which the food’s surface is heated first and then the heat gradually travels within. This is why foods don’t become crispy or browned like they would with other types of cooking since the air inside the microwave oven is room temperature. Another fact about microwaves is that ice can’t be melted in them as the water molecules in ice are so densely packed that microwaves aren’t able to make them move like they would in regular food.
RELATED STORIES:
https://www.verywellhealth.com/do-microwaves-cause-cancer-5077367
https://www.homesandgardens.com/advice/microwave-vs-air-fryer
TAKE ACTION:
https://www.bestbuy.com/site/home-appliances/microwaves/abcat0903000.c?id=abcat0903000
https://www.amazon.com/microwave-safe-bowl/s?k=microwave-safe+bowl