Introduction
Scientists in Japan have developed the use of golden nanoparticles in cancer treatment. This has allowed doctors to monitor exactly where the cancer medicine is injected into your body, how long it stays, and whether it is successful in reaching the tumor.
This new invention has allowed cancer treatment to become much more precise, and leads to a higher percentage of survival rates in hospitalized patients.
Extending Beyond Traditional Imaging Limitations
Before the use of this method, conventional imaging methods used flourescent dyes and radioisotopes to detect the nanoparticles. However, during circulation, these tracers tend to become less effective, and lead to inaccurate results or limited visualization.
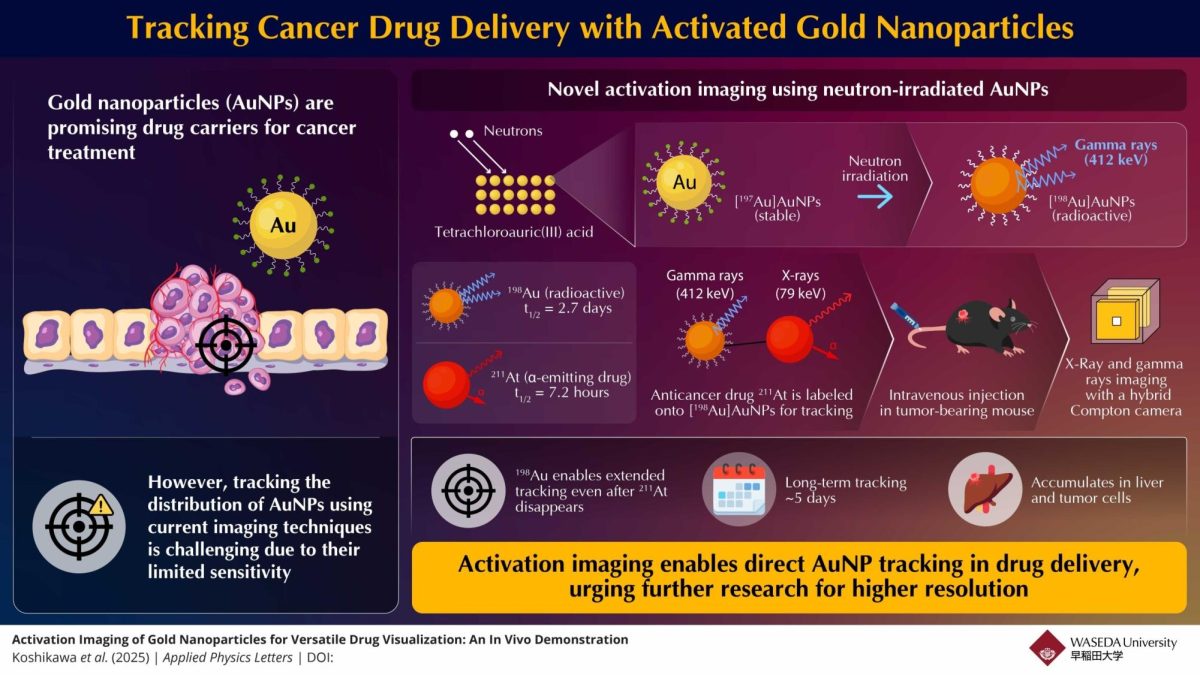
In an attempt to solve this issue, researchers at Waseda University in Japan have directly modified these AuNPs and made them detectable through X-rays and Gamma rays without having to rely on external tracers. To do this, they exposed the golden nanoparticles (197 Au) to sources of neutron radiation, transforming them into a radioactive form. The new radioactive form then gives out gamma rays, which can be easily detected from outside of the body.
Professor Jun Kataoka at Waseda University states that this technique changes toe material at an atomic level, but does not change the chemical properties. This allows for easy tracking of the material, but does not compromise the effectiveness of the nanoparticles.
Tracking Cancer Medicine With Newfound Precision
To test this new technology, scientists first used it on mice by injecting neutron-activated AuNPs into mice with cancer tumors. The enhanced imaging system was successfully able to track the nanoparticles, which confirmed their ability to provide a long-term monitoring system for the body.
Using this technique, researchers also explored how this method could track a cancer treatment drug with limited effectiveness known as astatine-211, or 211AT. This radio-therapeutic drug gives out alpha particles and X-rays, however its half-life of 7.2 hours made it much less effective. In an attempt to solve this problem, researchers labeled the 211AT with the radioactive AuNPs, forming 211AT-labeled AuNPs.
The use of 198Au has extended the tracking length of the drug to five days, and also extended the half-life to 2.7 days. This was a massive breakthrough, as scientists were able to monitor the drug much more easily and efficiently, helping the drug become more safe and effective in cancer treatment.
The Future of Cancer Treatment Observation
Tracking the delivery of cancer treatment drug delivery real-time is a major accomplishment in medical imaging. The research team believes that the neutron activation technique can be given a wider use by allowing it to monitor other kinds of nanoparticle-based drug delivery systems.
With more improvements, this innovative technology has the potential to become a widely used clinical tool, and make it become an even more precise drug monitoring system. The ability that this treatment possesses (enabling longer and more accurate tracking of therapeutic nanoparticles) may be the road to safer and more effective cancer treatment options in the near future.
RELATED STORIES:
https://interestingengineering.com/health/scientists-in-japan-develop-cancer-treatment-tracking
https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S2352507X24002543
https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC2874072/
https://www.eurekalert.org/news-releases/987526
TAKE ACTION:
Donate to the Cancer Research Institute:
https://www.cancerresearch.org/ways-to-give
Get a job at the National Cancer Institute:
https://www.cancer.gov/research/nci-role/cancer-research-workforce