Imagine an engine that doesn’t use the typical up-and-down motion of pistons but instead relies on a spinning motion—kind of like a dance instead of a hard workout. That’s exactly what a rotary engine does!
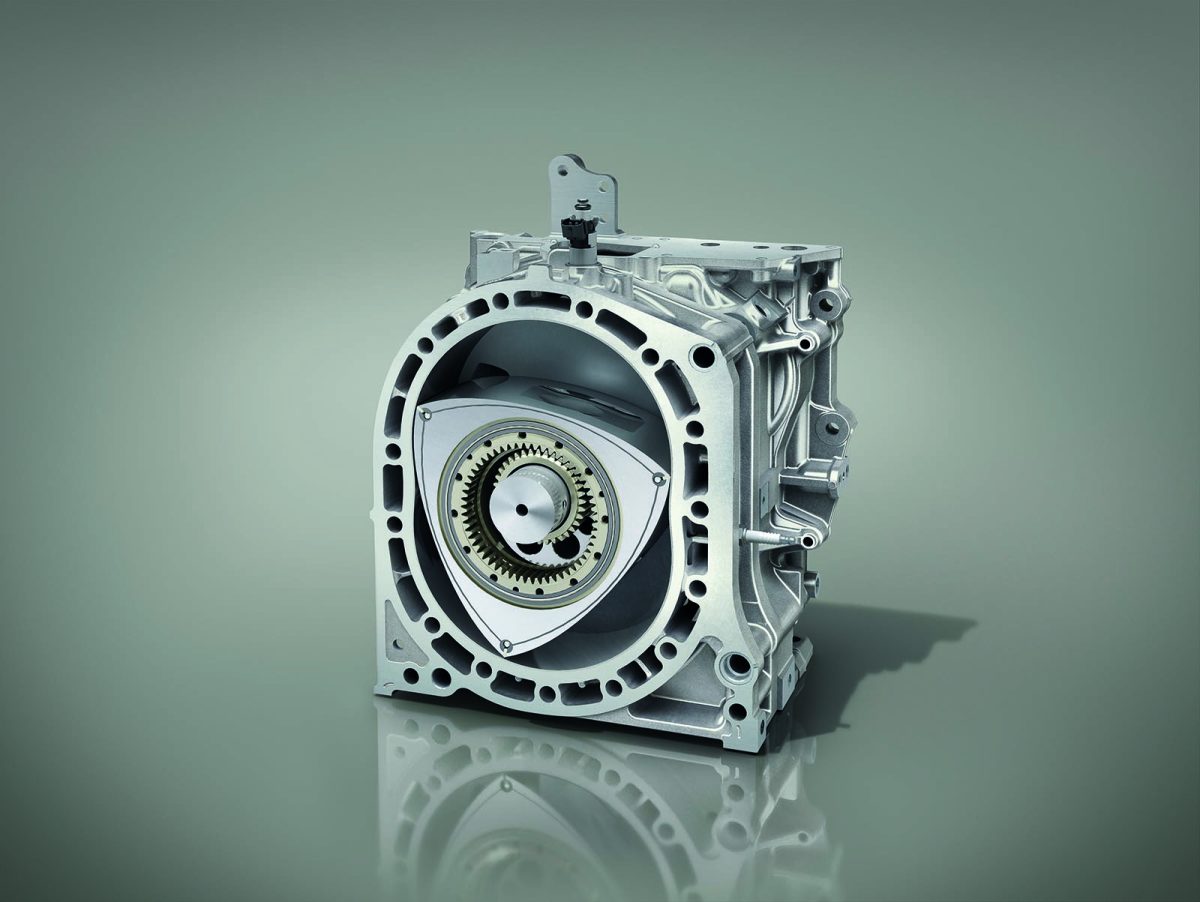
Unlike conventional engines, which use pistons moving inside cylinders, a rotary engine uses a triangular-shaped rotor that spins inside an oval-shaped chamber. This unique design makes the engine smaller, lighter, and smoother compared to traditional piston engines.
How it works
Instead of the familiar intake, compression, power, and exhaust strokes happening in separate cylinders like in a piston engine, a rotary engine completes these four steps in different sections of a single chamber as the rotor turns. This means fewer moving parts, which can lead to higher RPMs, a more compact design, and a smoother ride.
Engeeniering aspects
From an engineering perspective, the rotary engine is fascinating because it eliminates many of the inefficiencies of piston engines. There are no heavy connecting rods, crankshafts, or valves.
*Higher power-to-weight ratio – More power with a smaller size.
*Fewer vibrations – Since the rotor spins continuously rather than stopping and starting like a piston, there’s less internal stress.
*Simplicity – Fewer parts mean less mechanical complexity.
Related stories:
- https://www.liquidpiston.com/
- https://www.capomazda.com/blog/what-is-a-rotary-engine/?srsltid=AfmBOor61zrVVauSyLWgGWjDEbNlxyci-5-4nJidyQqdITO4a6wcH5DV
- https://www.redexadditives.com/blog/what-rotary-engines-cars/
Take action: